Table of Contents
Aim/Aim of Experiment
To find the Refractive Index of a Liquid by using Convex
Lens and Plane Mirror.
Apparatus/Material Required
- Convex lens
- A Plane mirror
- An optical Needle
- The clean transparent Liquid in beaker
- An Iron stand with base and clamp arrangement
- Pump line
- A plane glass slab
- A spherometer
- A half meter scale
Theory
Let us consider f1 and f2 are the focal lengths of glass convex lens and liquid lens respectively, Let F be the focal length of their combination then,
1/F=1/f1+1/f2 or 1/f2=1/F-1/f1
The Liquid lens formed is a plano-concave lens with R1=R, and R2=∞.
So, from lens maker’s formula,
1/f2=(n-1)[1/R1-1/R2]
we have 1/f2=(n-1)/R,
If R be the radius of curvature of the convex lens which is in contact with the liquid then the refractive index of the liquid is, n=1+R/f2.
Where n is the refractive index of the liquid and by putting the value of f2 then n can be calculated.
Diagram
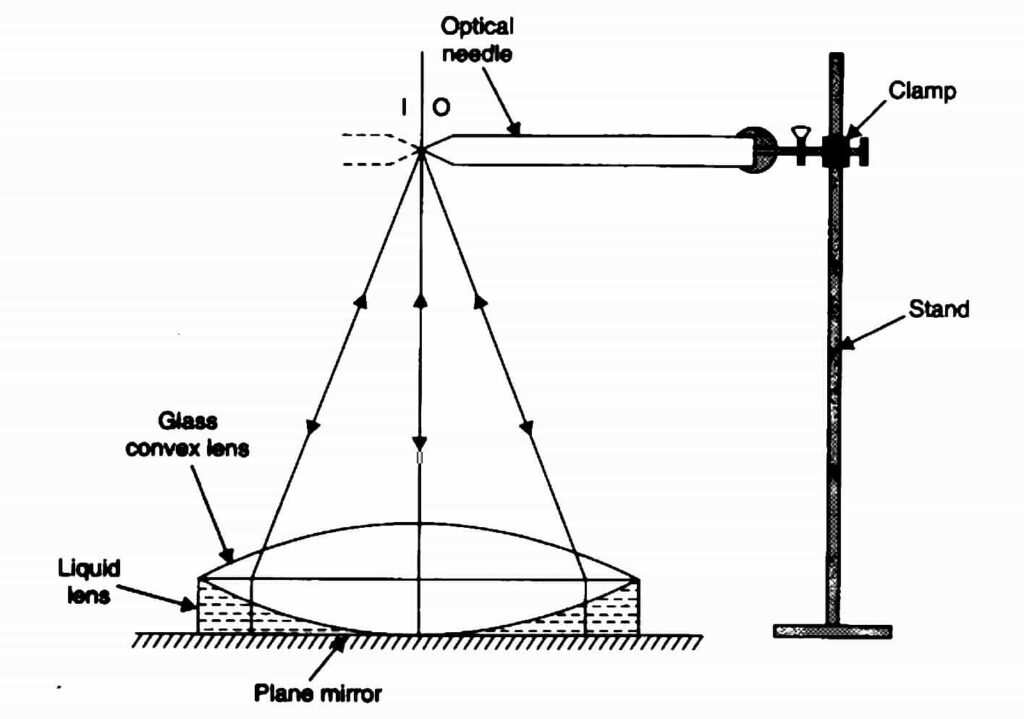
Procedure
For the Focal length of Canvex lens:
- Take a convex lens and find its rough focal length.
- Place the plane mirror horizontally on the base of the iron stand with its reflecting surface upward and place the convex lens on the plane mirror.
- Tight the screw of optical needle in the clamp of the stand and hold it horizontally above the lens at distance equal to its rough focal length.
- For the tip of the needle appears touching the tip of its image, bring the tip of the needle at the vertical principal axis of the lens.
- To remove parallax between tips of the needle and its image, move the needle up and down, so that image and object will be the same size.
- Measure the distance between tip and upper surface of the lens by using a plumb line and half metre scale, also measure the distance between tip and the surface of its plane mirror.
For the Focal length of the combination:
- Firstly remove the lens and take few drops of the given transparent liquid on the plane mirror.
- Now place the convex lens over the liquid with its same face in cantact with the liquid above as before.
- Repeat the Steps 5 and 6 of the above.
- Record your observations.
For the radius of curvature of convex lens surface:
- A plano-concave lens formed between the convex lens and the plane mirror so radius will be R1=R, and R2 =∞.
- From lens maker’s formula 1/f2=(n-1)[1/R1-1/R2 becomes 1/f2=(n-1)/R.
- Now the radius of curvature of the Canvex lens can be calculated by the formula R=(n-1)f2, where n is the refractive index of the liquid.
Observations
1. The rough focal length of the convex lens = 35 cm.
2. Table for distance of needle tip from Lens and Mirror:
| Arrangement | Distance of needle tip from lens surface x1 (cm) | Distance of needle tip from plane mirror x2 (cm) | Distance of needle tip Mean [x=(x1+x2)/2] | Focal Length x (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2a) | (2b) | (2c) | (3) |
| Without Liquid | 34.5 | 35 | 34.75 | f1=34.75 |
| With Liquid | 51.5 | 49 | 50.25 | F=50.25 |
3. The Radius of curvature of the Convex lens surface = 70 cm.
Calculations
1. Calculation for the focal length of liquid lens:
1/f2=1/F-1/f1,
putting the value of F and f1,
So, 1/f2 = 1/34.75-1/50.25
=0.02878-0.01990
1/f2 = 0.00888,
Hence, f2=1/0.00888 = 112.612.
2. Calculation for the refractive index of the liquid:
n=1+R/f2,
putting the value of R and F2,
n=[1+(70/112.612)]
= 1+0.6216
Hence, n = 1.6216.
Result
The refractive index of the liquid is, n=1.6216.
Precautions
- The liquid taken should be clean and transperant.
- The layer of liquid not be thick, so only a few drops of liquid should be taken.
- The parallax should be removed tip to tip.
Sources of Error
- The taken liquid not be quite transperant.
- The parallax may not be fully removed.
Class 12 Physics Practicals:
- To Determine Resistance Per cm of A Given Wire by Plotting A Graph for Potential Difference Versus Current
- To Find The Resistance of A Given Wire using The Metre Bridge and Hence Determine The Resistivity (Spacific Resistance) of It’s Material
- To Verify The Laws of Combination (Parallel) of Resistances using A Metre Bridge
- To Verify The Laws of Combination (Series) of Resistances Using A Metre Bridge
- To Compare The EMF of Two Given Primary Cells Using Potentiometer
- To Determine The Internal Resistance of A Given Primary Cell Using Potentiometer
- To Determine Resistance of A Galvanometer by Half-Deflection Method And To Find Its Figure of Merit
- To Convert The Given Galvanometer (of Known Resistance and Figure of Merit) Into a Voltmeter of Desired Range and To Verify the Same
- To Convert the Given Galvanometer (of Known Resistance and Figure of Merit) Into An Ammeter of Desired Range and to Verify the Same
- To Find The Frequency of The AC Mains With a Sonometer
- To Determine Angle of minimum Deviation for a given Prism by Plotting a Graph between Angle of Incidence & the Angle of Deviation
- To Determine Refractive Index of a Glass Slab Using a Travelling Microscope
- To Find Focal Length of A Convex Mirror Using A Convex lens
- To Find the Focal length of A Concave lens Using A Convex lens